Docker Port Mapping
When you create or run a container using docker create or docker run, it does not expose any of its ports to the outside world. To make a port available to services outside of Docker we use the --publish or -p flag. This creates a firewall rule which maps a container port to a port on the Docker host to the outside world.
-p 8080:80 Map TCP port 80 in the container to port 8080 on the Docker host.
-P Publish all exposed ports to random ports
This means that if any request comes to port 8080 of the docker host, it will route it to port 80 of the container.
Let's understand this with an example:
Suppose my local host's ip is 192.168.0.104. And NGINX container IP is 172.17.0.4. So with port mapping, we want to achieve-
Traffic from 192.168.0.104:3600 to go to 172.17.0.4:80
Run the below command to map the port-
learning-ocean:~ gaurav$ docker container run -itd -p 3600:80 nginx
0999e82d3da3b8e4f65ccffec307039645c8a72eef08fd8d7989dd84c85fcf09
learning-ocean:~ gaurav$
Let's try to access the NGINX with HostIP:Port
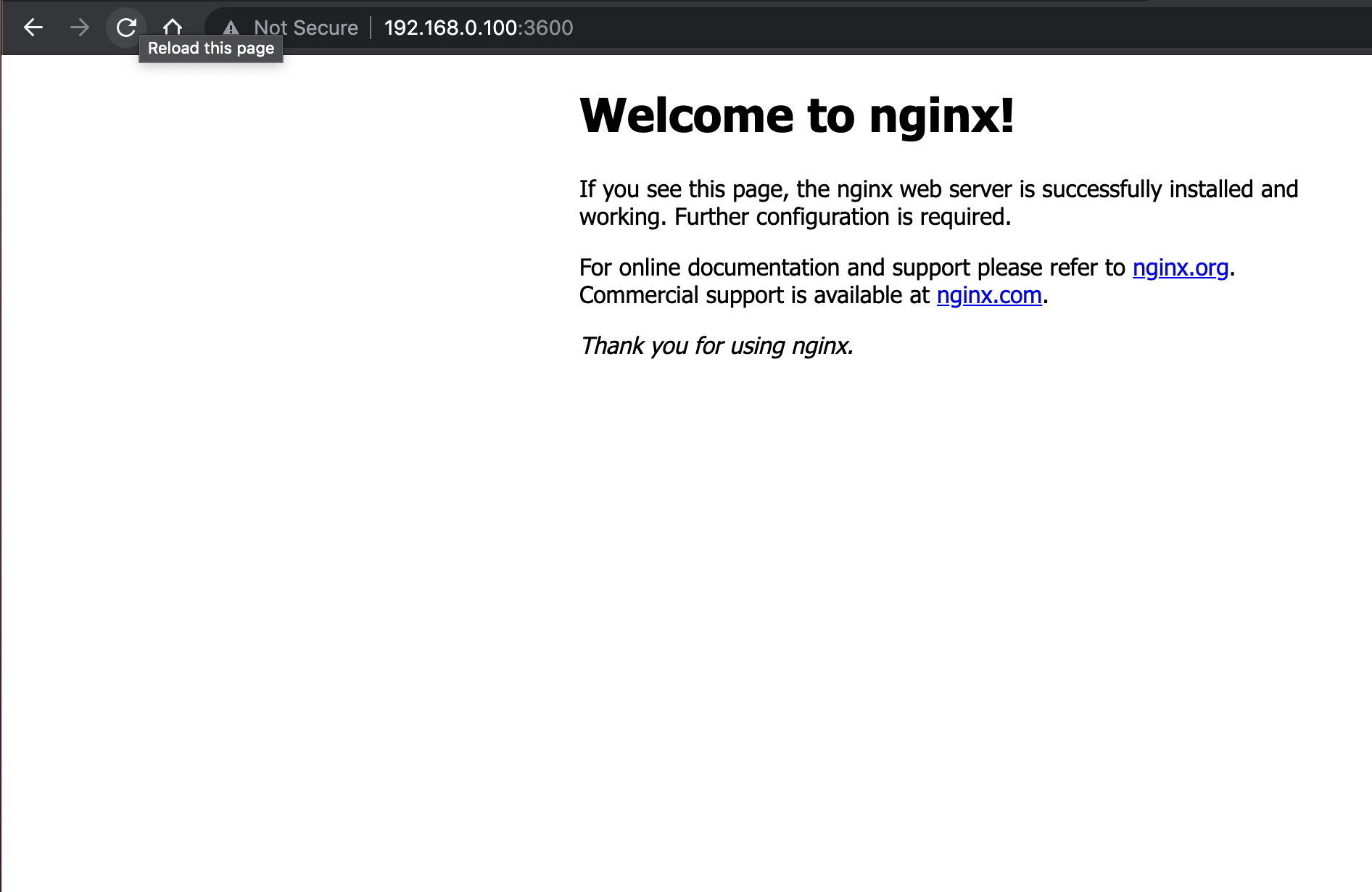
This way, we can expose our containers to the outside world.